Stay organised
Bookmark tricky questions or drop a doubt from the dashboard to revisit later.
Open dashboard →NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 3 – Fibre to Fabric
Kickstart revision for "Fibre to Fabric" with concise NCERT answers and quick tips.
Question 1
You must be familiar with the following nursery rhymes:(i) ‘Baa baa black sheep, have you any wool.’
(ii) ‘Mary had a little lamb, whose fleece was white as snow.’
Answer the following:
(a) Which parts of the black sheep have wool?
(b) What is meant by the white fleece of the lamb?
Answer
a) Wool obtained from hair called fleece of the sheep.
b) It refers to the white colour of their hairy skin.
Question 2
The silkworm is (a) a caterpillar, (b) a larva. Choose the correct option.(i) a (ii) b (iii) both a and b (iv) neither a nor b.
Answer
(iii) both a and b
Question 3
Which of the following does not yield wool?(i) Yak (ii) Camel (iii) Goat (iv) Woolly dog
Answer
The answer is (iv) Woolly dog
Question 4
.What is meant by the following terms?(i) Rearing (ii) Shearing (iii) Sericulture
Answer
i) Rearing is the process of keeping, feeding, breeding and giving medical care of animals like silkworm ,sheep and goat etc is called rearing
ii) Shearing is a process of removal of animal hair like sheep by using machines is called shearing
iii)the process of rearing of the silk worm to obtain good silk is called rearing.
Question 5
Given below is a sequence of steps in the processing of wool. Which are the missing steps? Add them.Shearing, __________, sorting, __________, __________, _________.
Answer
Shearing, Scouring, sorting, picking of burrs, dying of fibres, making of yarn
Question 6
Make sketches of the two stages in the life history of the silk moth which are directly related to the production of silk.Answer
Question 7
Out of the following, which are the two terms related to silk production?Sericulture, floriculture, moriculture, apiculture and silviculture.
Hints: (i) Silk production involves cultivation of mulberry leaves and rearing silkworms.
(ii)
Scientific name of mulberry is Morus alba
Answer
Sericulture and moriculture
Question 8
Match the words of Column I with those given in Column II:| Column-I | Column-I |
| 1. Scouring | (a) Yields silk fibres |
| 2. Mulberry leaves | (b) Wool yielding animal |
| 3. Yak | (c) Food of silkworm |
| 4. Cocoon | (d) Reeling |
| (e) Cleaning sheared skin |
Answer
| Column-I | Column-I |
| 1. Scouring | (e) Cleaning sheared skin |
| 2. Mulberry leaves | (c) Food of silkworm |
| 3. Yak | (b) Wool yielding animal |
| 4. Cocoon | (a) Yields silk fibres |
Question 9
Given below is a crossword puzzle based on this lesson. Use hints to fill in the blank spaces with letters that complete the words.Down
(D) 1 : Thorough washing
2 : Animal fibre
3 : Animal fibre
Across
(A) 1 : Keeps warm
2 : Its leaves are eaten by silkworms
3: Hatches from egg of moth
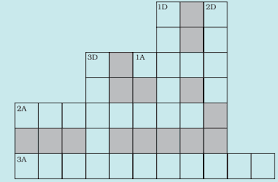
Answer
Down:
1D. Scour
2D. Silk
3D. Fibre
Across
1A. Wool
2A. Mulberry
3A. Caterpillar
Chapter 1: Nutrition in Plants
Chapter 2: Nutrition in Animals
Chapter 5: Acids, Bases and Salts
Chapter 6: Physical and Chemical Changes
Chapter 7: Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
Chapter 8: Winds, Storms and Cyclones
Chapter 10: Respiration in Organisms
Chapter 11:Transportation in Animals and Plants
Chapter 12:Reproduction in Plants
Chapter 14: Electric Current and Its Effects
Chapter 16:Water: A Precious Resource
More resources
Looking for structured practice? Jump into worksheets or the streak tracker.
Download worksheets →